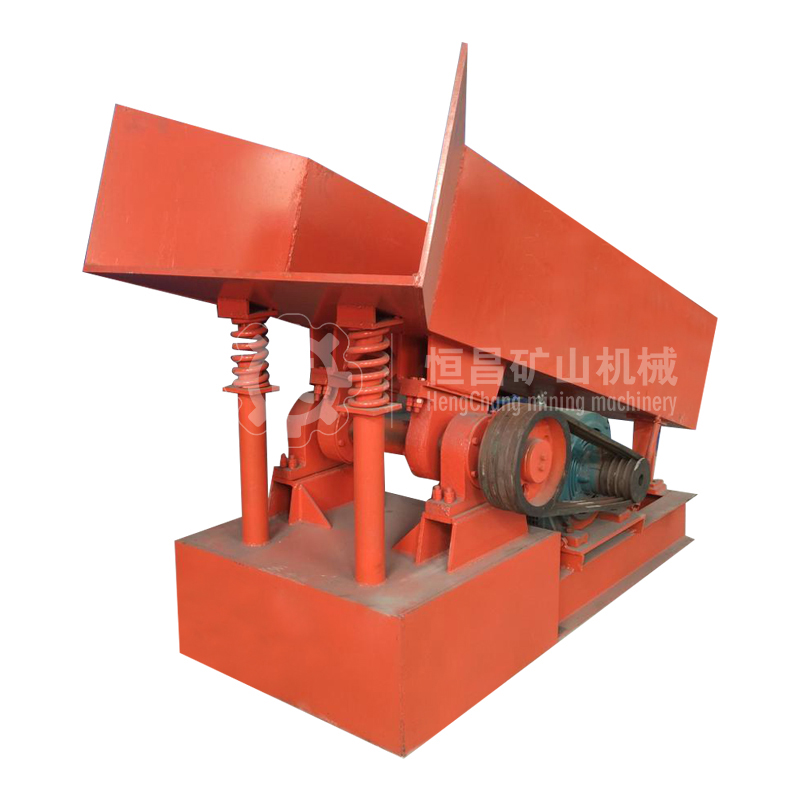
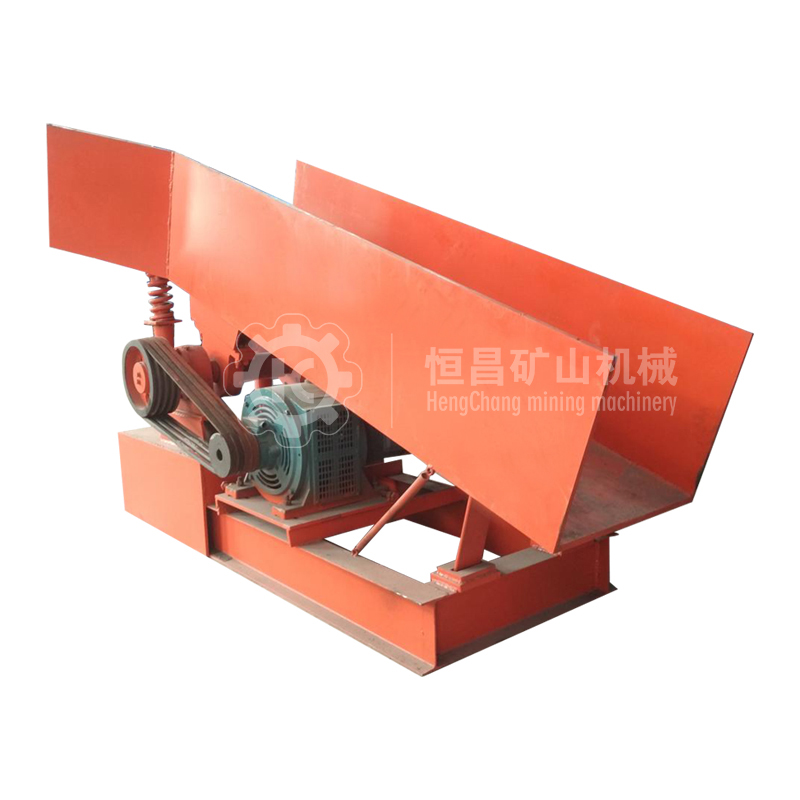
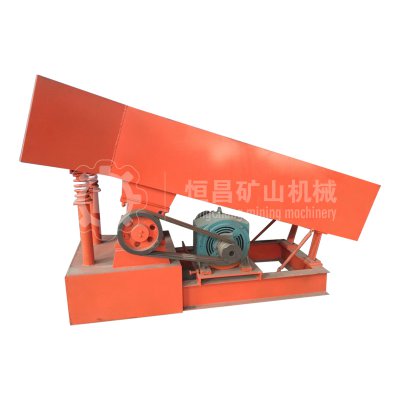
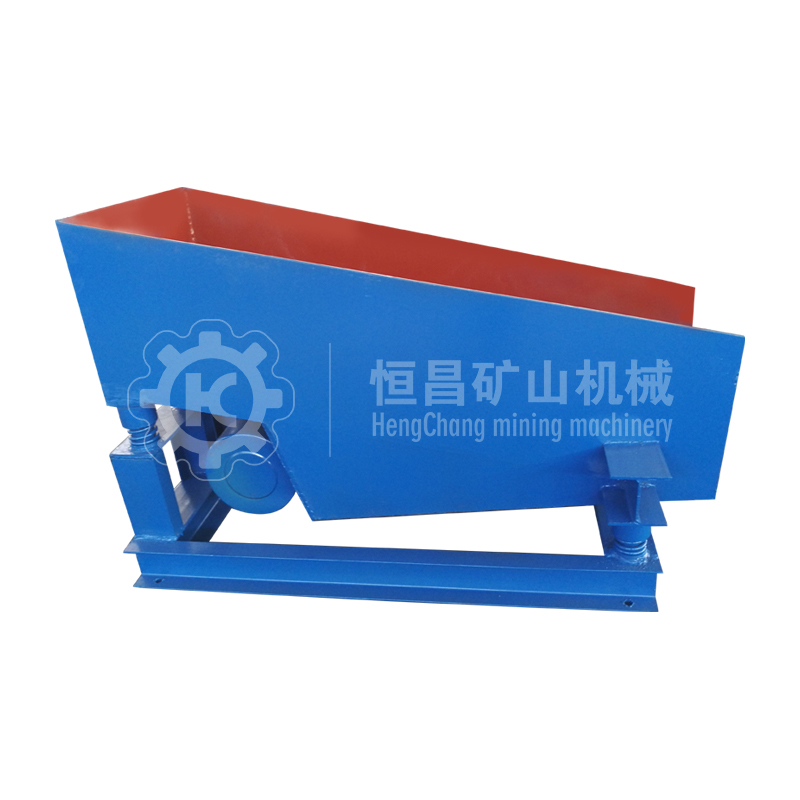
Feeder Machine
Product details
Application Rang:
Electromagnetic vibration feeder can be widely used in metallurgy, coal, power, machinery, chemical industry, building materials, light industry and grain industry and mining enterprises.For example, from silo discharge, to belt conveyor, bucket elevator feeding, to crusher, ball mill feeding, in the packaging system to do quantitative feeding, in the batching system to do uniform and continuous batching.
Advantages and Characteristics:
(1)The half-wave rectifier control circuit can steplessly adjust the feeding quantity in the rated output, and can be used in the automatic control production process to realize the production automation.
(2)The automatic amplitude stabilization control system can be provided according to the user's requirements, and the amplitude fluctuation of feeder is less than or equal to 3%. Intelligent feeding can be realized by matching the computer control box with high stability.
(3)The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, light weight, no need of lubrication and convenient maintenance.
(4) Because of the near resonance principle, the energy consumption is low. The material is slightly thrown in the trough, and the wear of the trough is small.
working principle:
Electromagnetic vibrating feeder manufacturer is mainly used to evenly and continuously feed materials to the conveyor belt, bucket elevator, crusher, ball mill, etc. It can be also adopted to realize the automatic production process. This machine is not suitable to convey wet and sticky materials.
During the use of the electromagnetic feeder, the exciting force can be adjusted to change and control the flow rate, so the adjustment is convenient, the flow rate is stable, the noise is low, the power consumption is small, there is no punching phenomenon, and the machine has the characteristics of lightweight, small volume, convenient maintenance, etc. If the closed structure is adopted, dust overflow and environmental pollution can be prevented.
Type | Model | Capacity (t/h) | Max.feeding size | Amplitude (mm) | Voltage (V) | Effective power(Kw) | |
0° | -10° | ||||||
Standard | GZ1 | 5 | 7 | 50 | 1.75 | 220 | 0.06 |
GZ2 | 10 | 14 | 50 | 0.15 | |||
GZ3 | 25 | 35 | 75 | 0.2 | |||
GZ4 | 50 | 70 | 100 | 0.45 | |||
GZ5 | 100 | 140 | 150 | 0.65 | |||
GZ6 | 150 | 210 | 200 | 1.5 | 380 | 1.2 | |
GZ7 | 250 | 350 | 250 | 3 | |||
GZ8 | 400 | 560 | 300 | 4 | |||
GZ9 | 600 | 840 | 350 | 5.5 | |||
GZ10 | 750 | 1050 | 500 | 4*2 | |||
GZ11 | 1000 | 1400 | 500 | 5.5*2 | |||